Have you ever wondered what powers the machines and vehicles you rely on every day? The answer lies in something called an engine.
But what exactly is an engine, and how many types are there? Understanding this can change the way you see cars, motorcycles, and even airplanes. You’ll discover what an engine really is and explore the different types that keep the world moving.
By the end, you’ll have a clear idea that can help you make smarter choices—whether you’re buying a vehicle or just satisfying your curiosity. Keep reading to unlock the engine secrets that everyone should know.
Engine Basics
Engines are at the heart of many machines. They provide the power needed to move cars, planes, and even boats. Understanding the basics of engines helps us appreciate how machines work around us.
Engines come in many types, but all share some common principles. Knowing these can make it easier to learn about different engines and their uses.
What Is An Engine
An engine is a machine that changes energy into motion. It takes fuel or power and turns it into mechanical work. This work then moves parts or the whole machine.
Engines are found in vehicles, tools, and many devices. They are essential for modern life and technology.
How Engines Work
Engines work by burning fuel or using electricity to create force. This force moves parts inside the engine, like pistons or rotors. The movement then powers the machine.
Some engines use fuel like gasoline or diesel. Others use electricity or air pressure. Each type uses a different process to create movement.
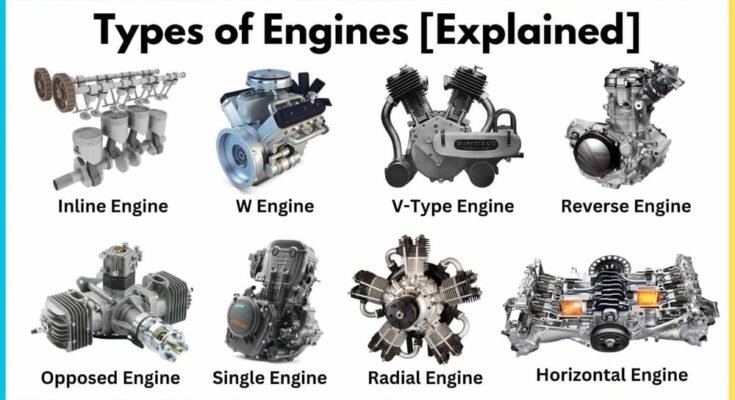
Types Of Engines
Engines play a vital role in powering machines and vehicles. They convert energy into motion. Different types of engines use various methods to create power. Understanding these types helps us see how machines work. The main types include internal combustion, external combustion, and electric engines.
Internal Combustion Engines
Internal combustion engines burn fuel inside the engine itself. This process creates hot gases that push pistons. Cars, motorcycles, and many machines use this engine type. It is compact and efficient for small vehicles. Gasoline and diesel are common fuels used here.
External Combustion Engines
External combustion engines burn fuel outside the engine. The heat produced then moves a working fluid like steam. This steam drives pistons or turbines to create motion. Steam engines and some power plants use this method. They are larger and less common in vehicles.
Electric Engines
Electric engines use electricity to produce motion. They work quietly and do not burn fuel. Electric motors are common in electric cars and appliances. They offer smooth and instant power delivery. Batteries or power grids usually supply their energy.
Internal Combustion Engine Varieties
Internal combustion engines power most vehicles worldwide. They burn fuel inside the engine to create energy. This energy moves pistons or rotors to produce motion. Many types of internal combustion engines exist, each with unique designs and uses. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right engine for different needs.
Petrol Engines
Petrol engines use gasoline as fuel. They mix air and fuel before ignition. Spark plugs ignite the mixture inside the cylinder. These engines run smoothly and are quieter. They are common in cars and motorcycles. Petrol engines work best at higher speeds.
Diesel Engines
Diesel engines use diesel fuel. They compress air to a high temperature. Diesel fuel ignites from the hot air without spark plugs. Diesel engines are more efficient and have higher torque. They are often used in trucks and heavy vehicles. These engines last longer but can be noisier.
Two-stroke Vs Four-stroke
Two-stroke engines complete a power cycle in two piston strokes. They are simpler and lighter. These engines produce more power but pollute more. Four-stroke engines take four piston strokes per cycle. They are more fuel-efficient and cleaner. Four-stroke engines are common in cars and lawnmowers.
Rotary Engines
Rotary engines use a triangular rotor instead of pistons. The rotor spins inside a chamber to create power. These engines are compact and smooth-running. They have fewer moving parts than piston engines. Rotary engines are rare but found in some sports cars.

External Combustion Engine Varieties
External combustion engines use heat from outside to power the engine. These engines burn fuel in a separate chamber. The heat produced moves a working fluid like steam or gas. This fluid then drives the engine’s moving parts. External combustion engines offer smooth and steady power.
Steam Engines
Steam engines are one of the oldest types of external combustion engines. They burn coal, wood, or oil to boil water. The steam created pushes pistons or turns turbines. This motion powers trains, ships, and early factories. Steam engines were key during the industrial revolution. They provide high torque at low speeds.
Stirling Engines
Stirling engines work by heating and cooling a gas inside the engine. The gas expands when heated and contracts when cooled. This movement drives pistons or other mechanical parts. Stirling engines run quietly and use different heat sources. They are efficient and produce low pollution. These engines are used in submarines and solar power systems.
Electric Engine Types
Electric engines are key parts of many machines today. They convert electrical energy into mechanical power. This power moves cars, fans, tools, and many other devices. Electric engines come in different types. Each type works in a special way and suits specific uses.
Dc Motors
DC motors run on direct current electricity. They are simple and easy to control. These motors change electric power into spinning motion. DC motors are common in toys, small machines, and cars. They offer good speed control and strong starting power.
Ac Motors
AC motors use alternating current electricity. They are often found in home appliances and industry machines. These motors are reliable and need less maintenance. AC motors come in many sizes and types. They are good for steady and long-time work.
Brushless Motors
Brushless motors do not use brushes for power transfer. This makes them more efficient and quieter. They last longer because there is less wear. Brushless motors are popular in drones, electric cars, and computers. They provide smooth and precise control of speed.
Engine Components
An engine works through many important parts. These parts work together to create power. Understanding these components helps you see how engines run.
Each part has a role in turning fuel into motion. The engine parts must be strong and fit well. Let’s explore the main engine components.
Cylinder And Pistons
The cylinder is a hollow tube where fuel burns. Inside the cylinder, the piston moves up and down. The piston’s movement creates pressure to turn the engine’s power.
Pistons are usually made of metal to handle heat. The fit between the piston and cylinder must be tight. This tight fit keeps the pressure inside for power.
Crankshaft And Camshaft
The crankshaft changes the piston’s up-and-down movement into spinning power. This spinning motion drives the car’s wheels. The crankshaft is a strong metal shaft inside the engine.
The camshaft controls the opening and closing of valves. It works with the crankshaft but moves slower. The camshaft ensures the engine breathes properly by timing the valves.
Valves And Spark Plugs
Valves open and close to let air in and out of the cylinder. Intake valves bring air and fuel. Exhaust valves push out burned gases.
Spark plugs create a small spark to ignite the fuel-air mix. This spark starts the combustion inside the cylinder. Without spark plugs, the engine cannot run.
Engine Performance Factors
Engine performance depends on many key factors. These factors determine how well an engine works for different tasks. Understanding them helps you choose the right engine type. It also shows how engines meet the needs of power, fuel use, and environmental rules.
Power And Torque
Power is the engine’s ability to do work over time. It affects how fast a vehicle can go. Torque is the twisting force the engine produces. It helps with moving heavy loads and quick starts. Both power and torque are important for engine strength.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency shows how much fuel an engine uses for distance. A good engine uses less fuel to save money. It also means fewer stops at gas stations. Efficient engines help reduce fuel costs and pollution. This makes them better for daily use.
Emissions And Environmental Impact
Engines release gases when running. Some gases harm the air and health. New engines use technology to lower harmful emissions. Cleaner engines protect the environment and meet laws. Reducing emissions is key for future engine designs.

Choosing The Right Engine
Choosing the right engine is key to getting the best performance and efficiency. Different engines suit different tasks. Picking the right one saves money and reduces problems later. Consider the engine’s purpose and environment before making a choice.
Applications And Use Cases
Engines are built for specific uses. Some work well in cars, others in boats or machines. Small engines fit lawnmowers or generators. Large engines power trucks and ships. Knowing the engine’s use helps find the perfect match.
For example, a diesel engine suits heavy-duty vehicles. Gasoline engines work best for passenger cars. Electric engines are ideal for quiet, eco-friendly machines. Each type fits certain needs and conditions.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Every engine type has pros and cons. Gasoline engines start quickly and run smoothly. They cost less but use more fuel. Diesel engines last longer and use fuel efficiently. They are louder and cost more upfront.
Electric engines are clean and quiet. They need charging and have limited range. Hybrid engines mix fuel and electric power. They balance fuel use and power but can be complex to fix.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Engine And How Does It Work?
An engine is a machine that converts fuel into mechanical energy. It powers vehicles by burning fuel to create motion. Engines can be internal or external combustion types. They drive cars, machines, and many tools efficiently and reliably.
What Are The Main Types Of Engines?
The main types of engines are internal combustion engines and external combustion engines. Internal engines burn fuel inside cylinders. External engines burn fuel outside, like steam engines. Engines also vary by fuel type, such as petrol, diesel, or electric motors.
How Do Internal Combustion Engines Differ From External Ones?
Internal combustion engines burn fuel inside the engine’s cylinders, creating power directly. External combustion engines burn fuel outside the engine, usually producing steam to drive pistons. Internal engines are common in cars; external ones are used in older trains and industrial machines.
Which Engines Are Most Common In Vehicles Today?
Most vehicles use internal combustion engines powered by petrol or diesel. These engines efficiently convert fuel into motion. Electric engines are rising but still less common. Hybrid engines combine electric and combustion types for better fuel economy.
Conclusion
Engines power many machines in daily life. They come in various types, each serving a purpose. Some use gasoline, others use electricity or diesel. Knowing engine types helps us understand how machines work. This knowledge can guide choices in vehicles and tools.
Engines keep the world moving forward, quietly and efficiently. Learning about them opens doors to better decisions and curiosity. Engines are more than just parts; they are the heart of machines.