Have you ever wondered what makes a turbo jet engine roar to life and power an aircraft through the sky? Understanding how a turbo jet engine works can seem complicated, but it doesn’t have to be.
This guide will break down the key parts and processes in a simple way, so you can grasp exactly how these powerful machines turn fuel into thrust. By the end, you’ll see why turbo jet engines are marvels of engineering and how they deliver maximum performance.
Ready to unlock the secrets behind these incredible engines? Let’s dive in!

Jet Engine Basics
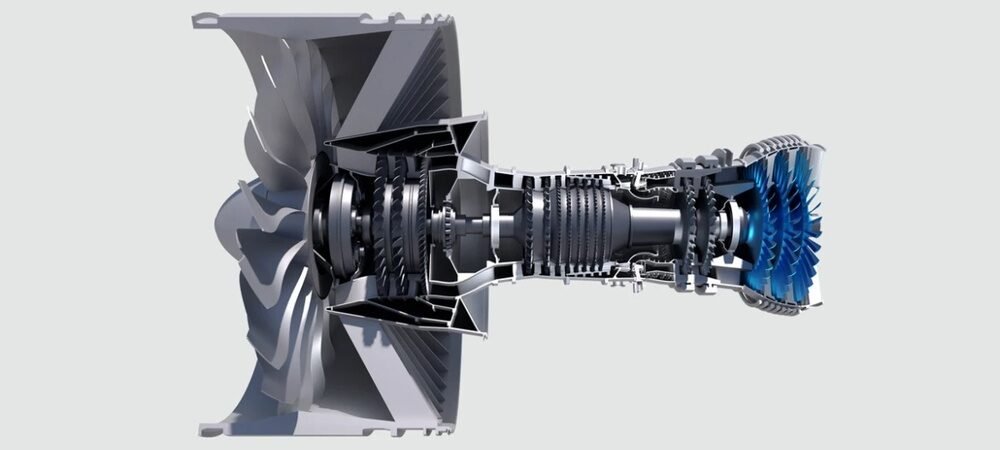
A turbojet engine is a powerful machine. It turns air into thrust to push an aircraft forward. Understanding how it works starts with learning its main parts and how air moves inside it.
The engine takes in air, compresses it, mixes it with fuel, and burns the mixture. This creates hot gases that shoot out the back. This push moves the plane through the sky.
Key Components
The turbojet has several important parts. First, the intake pulls air into the engine. Then, the compressor squeezes this air to raise its pressure. Next, the combustion chamber burns fuel with the compressed air. After that, the turbine extracts energy from the hot gases to power the compressor. Finally, the exhaust nozzle pushes the gases out fast, creating thrust.
Each component works in a cycle. They rely on each other to keep the engine running smoothly. Without one part, the engine cannot produce thrust.
Airflow Process
Air enters the engine through the intake. The compressor increases air pressure by squeezing it. This makes the air denser and hotter.
Fuel mixes with the compressed air in the combustion chamber. This mixture burns and expands quickly. Hot gases flow through the turbine, making it spin. The turbine powers the compressor using this energy.
Finally, the gases exit through the exhaust nozzle. They push backward, moving the plane forward. This process repeats many times each second to keep the engine running.
Compression Stage
The compression stage is a vital part of a turbojet engine. It prepares the air for combustion by increasing its pressure. This process helps the engine produce more thrust efficiently.
Air enters the compressor at low pressure and exits at high pressure. Compressing the air makes the fuel burn better and creates more power. Without this stage, the engine cannot work properly.
Role Of Compressors
Compressors squeeze the air to raise its pressure. This step is key for engine performance. Higher pressure air mixes well with fuel. It helps the engine burn fuel fully and produce strong thrust. Compressors keep the airflow steady and smooth through the engine. They also reduce the temperature of the incoming air slightly before combustion.
Types Of Compressors
Two main types of compressors exist in turbojet engines: axial and centrifugal. Axial compressors push air straight through many spinning blades. They are common in modern engines. Centrifugal compressors throw air outward by spinning fast. These are simpler and used in smaller engines. Some engines combine both types for better efficiency. Each type has strengths depending on engine size and speed.
Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber is a key part of a turbo jet engine. It is where air and fuel mix and burn. This burning creates hot gas that powers the engine. The design of the chamber helps keep the fire steady and strong. It must handle very high temperatures and pressure safely.
Inside the combustion chamber, air from the compressor enters at high speed. Fuel is added and then ignited. The energy from burning fuel pushes the turbine blades. This process keeps the engine running and produces thrust for the aircraft.
Fuel Injection
Fuel injection is the process of spraying fuel into the combustion chamber. The fuel is atomized into tiny droplets. This helps it mix well with the incoming air. Good mixing is essential for efficient burning. Injectors must deliver the right amount of fuel precisely. Too much or too little fuel can harm engine performance.
Fuel injectors are designed to work under extreme heat and pressure. They must prevent leaks and blockages. The fuel sprays in patterns to fill the chamber evenly. This helps maintain a steady and smooth flame.
Ignition Process
The ignition process starts the burning of the fuel-air mix. A spark plug or igniter creates a spark inside the chamber. This spark lights the fuel and air mixture quickly. Once the flame starts, it continues on its own. The engine’s airflow supports the burning process.
Ignition must be reliable at all times, especially during engine start. If ignition fails, the engine will not run properly. The spark must be strong and last long enough to start the combustion. Proper ignition ensures the engine reaches full power safely.

Turbine Function
The turbine is a key part of a turbo jet engine. It helps convert hot gases into useful power. The turbine takes the energy from the fast-moving gases and uses it to keep the engine running smoothly. This part works with great precision to keep the engine efficient and strong.
Understanding how the turbine works helps us see the full picture of turbo jet engine operation. It plays a vital role in managing energy flow inside the engine.
Energy Extraction
The turbine extracts energy from the hot gases produced by burning fuel. These gases expand quickly and hit the turbine blades. The force from these gases turns the turbine. This process lowers the gas pressure and temperature. The energy taken from the gases is used to power other parts of the engine.
Driving The Compressor
The turbine connects directly to the compressor through a shaft. When the turbine blades spin, they turn the compressor blades. The compressor then squeezes air and pushes it into the combustion chamber. This continuous cycle keeps the engine working. Without the turbine driving the compressor, the engine cannot produce thrust.
Exhaust And Thrust
The exhaust and thrust are the heart of a turbo jet engine’s power. The engine burns fuel and air, creating hot gases. These gases rush out of the back of the engine at high speed. This fast flow of gas pushes the airplane forward. The design of the exhaust system plays a big role in how well the engine works.
Nozzle Design
The nozzle shapes the flow of the hot gases as they exit the engine. It narrows down to speed up the gas flow. Faster gas means more force pushing backward. This force pushes the plane forward. The nozzle must handle very high temperatures and pressures. Its shape can change depending on the flight speed and altitude. A well-designed nozzle improves engine efficiency and power.
Creating Forward Motion
The fast gases leaving the nozzle create thrust. Thrust is the force that moves the airplane ahead. The engine pushes gases backward to push the plane forward. This follows Newton’s third law: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The stronger the gas flow, the more thrust is created. This thrust helps the plane take off, climb, and cruise through the sky.
Efficiency Factors
Efficiency factors play a key role in how well a turbo jet engine performs. These factors help the engine use fuel and air to produce maximum thrust with minimum waste. Small improvements in efficiency can lead to big gains in power and fuel savings. Understanding these factors helps engineers build better engines and keeps flights smooth and cost-effective.
Material Advances
Materials used in turbo jet engines must handle extreme heat and pressure. New alloys and composites resist high temperatures. This allows the engine to run hotter and produce more thrust. Stronger materials reduce wear and tear. They also help the engine last longer. These advances lower maintenance costs and improve overall engine efficiency.
Design Improvements
Engine design changes boost efficiency by improving airflow and combustion. Better blade shapes reduce air resistance and increase thrust. Advanced cooling methods keep parts from overheating. Compact designs save weight without losing power. Engineers use computer models to test designs before building. These improvements make engines lighter, faster, and more fuel-efficient.
Common Applications
Turbo jet engines power many types of aircraft. Their design helps planes fly fast and high. These engines work best in specific fields. They provide strong thrust and efficiency. Below are the common ways turbo jet engines are used.
Commercial Aviation
Most large passenger planes use turbo jet engines. These engines give the thrust needed for long flights. They help planes reach high speeds and altitudes. Turbo jets keep air travel smooth and safe. Airlines rely on them to move people worldwide.
Fuel efficiency is key for airlines. Turbo jets balance power and fuel use well. They allow flights to cover thousands of miles nonstop. Passengers benefit from faster travel times. Airports also support these engines with proper services.
Military Use
Military jets depend heavily on turbo jet engines. These engines deliver high speed and quick response. Fighter planes and bombers use turbo jets to perform missions. Speed helps pilots evade threats and attack targets.
Turbo jets in military aircraft offer strong power in combat. They enable rapid takeoffs and agile maneuvers. These engines handle harsh conditions and long missions. Military forces value reliability and performance above all.
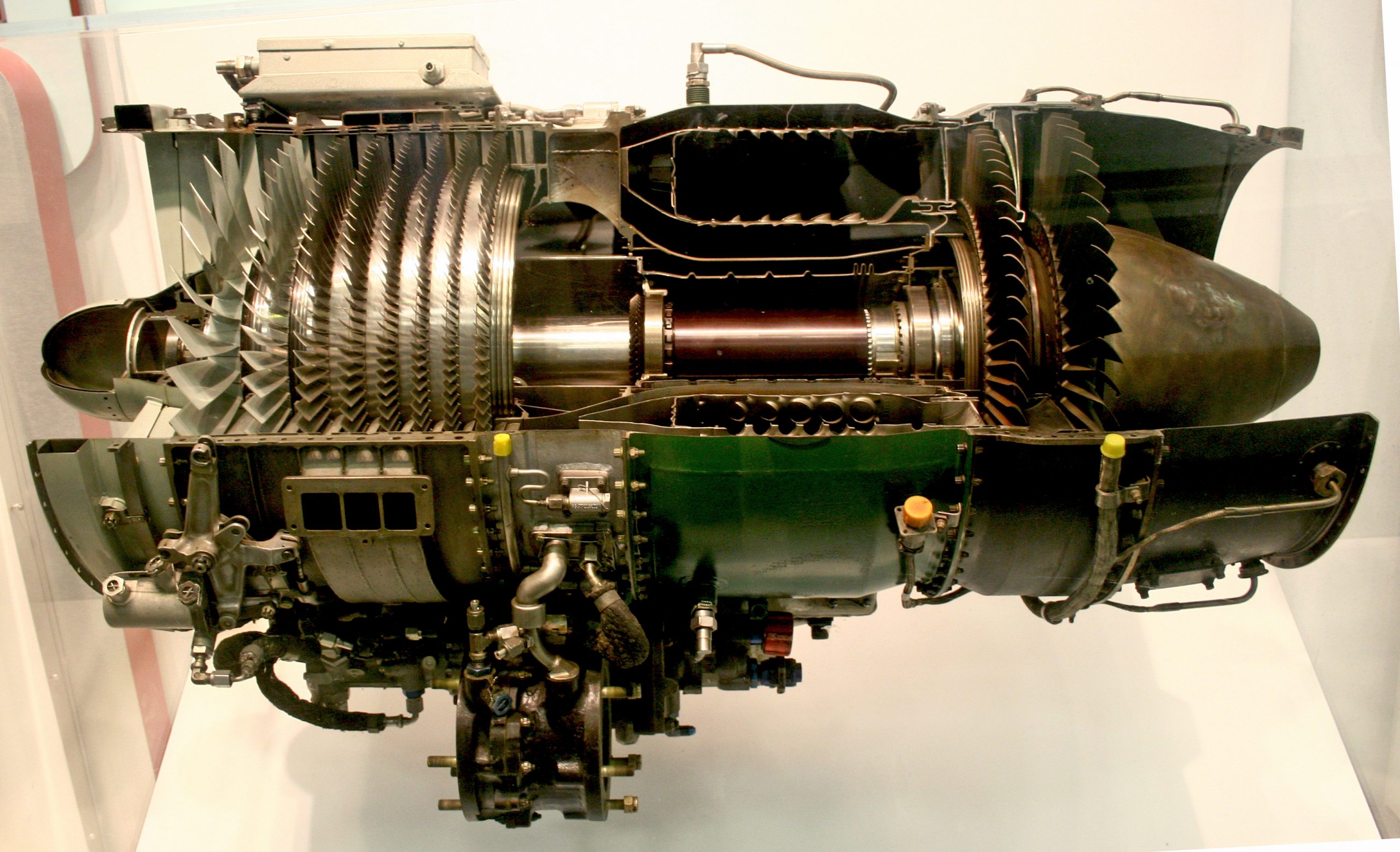
Maintenance And Safety
Maintenance and safety are vital for turbo jet engines. Proper care keeps the engine running smoothly. It also prevents accidents and costly repairs. Regular checks catch problems early. Safety measures protect both the engine and the people operating it.
Inspection Procedures
Inspection starts with visual checks. Look for cracks, leaks, or worn parts. Use special tools to measure blade damage. Inspect fuel lines and electrical connections. Clean filters and remove debris. Follow the manufacturer’s checklist carefully. Regular inspections ensure the engine works efficiently.
Troubleshooting Issues
Troubleshooting begins with identifying unusual noises or vibrations. Check engine temperature and pressure readings. Look for fuel flow problems or ignition failures. Use diagnostic tools to scan for faults. Replace damaged parts immediately. Troubleshooting helps fix issues before they grow bigger. It keeps the engine safe and reliable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Parts Of A Turbo Jet Engine?
A turbo jet engine consists of an air intake, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, and exhaust nozzle. Each part works in sequence to compress air, mix it with fuel, ignite the mixture, and expel exhaust gases to generate thrust efficiently.
How Does A Turbo Jet Engine Produce Thrust?
Thrust is produced by accelerating exhaust gases out of the engine. Compressed air mixed with fuel combusts, expanding rapidly. This high-speed exhaust exits the nozzle, pushing the engine forward according to Newton’s third law of motion, providing effective propulsion for aircraft.
Why Is Compressor Important In Turbo Jet Engines?
The compressor increases air pressure entering the combustion chamber. Higher pressure allows better fuel-air mixing and efficient combustion. This results in greater power output and improved fuel efficiency, making the compressor critical for the engine’s performance.
How Does A Turbine Work In A Turbo Jet Engine?
The turbine extracts energy from hot combustion gases. It powers the compressor by spinning its blades using exhaust gas energy. This process ensures continuous air compression and fuel combustion, maintaining steady engine operation and thrust production.
Conclusion
Turbo jet engines power many aircraft with strong, fast thrust. They work by pulling in air, compressing it, burning fuel, and pushing hot gases out. This process creates the force that moves planes forward. Understanding these steps helps you see how engines deliver speed and power.
Simple parts work together to keep planes flying safely and efficiently. Knowing this can make you appreciate the technology behind flight. The turbo jet remains a key invention in aviation history.