Have you ever wondered what makes diesel engines so powerful and reliable? Whether you drive a truck, use heavy machinery, or simply want to understand your vehicle better, knowing how diesel engines work can give you a new appreciation for their strength and efficiency.
You’ll discover the simple steps behind the diesel engine’s operation and why it stands out from other engines. By the end, you’ll have clear answers that make this complex topic easy to grasp—and maybe even impress your friends with your new knowledge.
Ready to dive in? Let’s get started!
Diesel Engine Basics
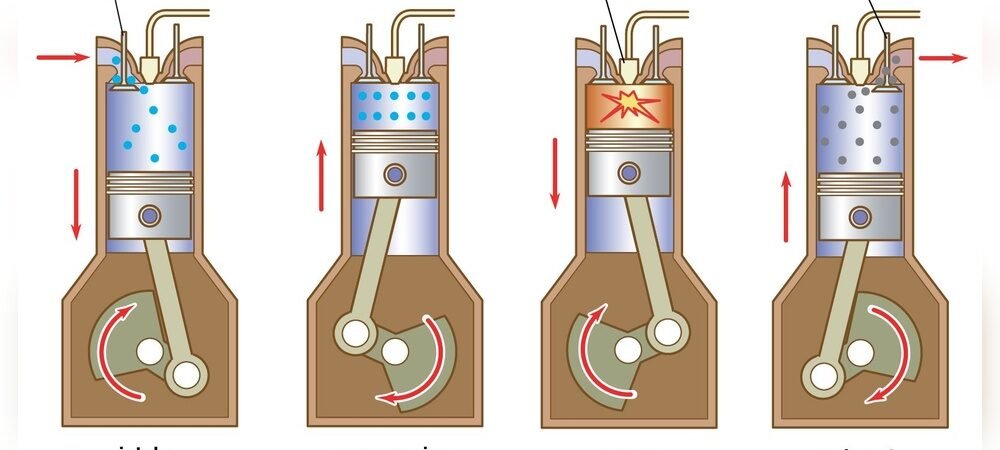
Diesel engines power many vehicles and machines worldwide. They run differently from gasoline engines. Understanding the basics helps explain their strong performance and fuel efficiency. Diesel engines use air and fuel in a unique way to create power. This section covers the key parts and how the combustion process works.
Key Components
Several main parts make a diesel engine work. The cylinder is where fuel burns and power forms. Pistons move inside cylinders to transfer energy. The fuel injector sprays diesel into the cylinder. The air intake brings fresh air to mix with fuel. The exhaust valve lets out burnt gases. The crankshaft turns the piston movement into usable power. Each component plays a vital role in engine function.
How Combustion Happens
Diesel engines start by drawing air into the cylinder. The air compresses tightly, making it very hot. Then, diesel fuel sprays into the hot air. The fuel ignites due to high temperature. This ignition causes a small explosion. The explosion pushes the piston down, creating power. This process repeats many times per second to keep the engine running. Combustion in diesel engines is efficient and strong.
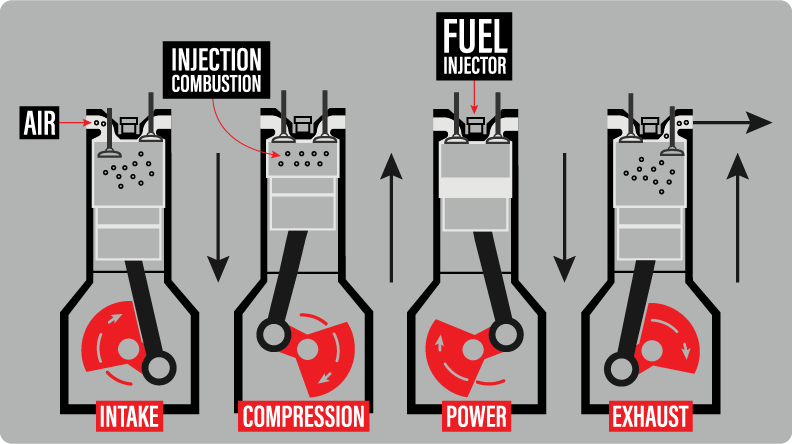
Power Generation Process
The power generation process in diesel engines turns fuel into motion. It happens in a few key steps inside the engine cylinder. Each step plays a role in creating the power that moves vehicles and machines. Understanding these steps helps explain how diesel engines work efficiently and strongly.
Intake And Compression
First, air enters the cylinder through the intake valve. The piston moves down, drawing air inside. Next, the piston moves up, compressing the air tightly. This compression raises the air temperature to a very high level. No fuel is added yet. The hot, compressed air is ready for the next step.
Fuel Injection And Ignition
Fuel injectors spray diesel fuel into the hot, compressed air. The fuel instantly ignites from the heat without a spark. This sudden combustion creates high pressure inside the cylinder. The pressure pushes the piston down with great force. This movement produces the engine’s power to turn wheels or equipment.
Exhaust Stroke
After the power stroke, the piston moves up again. It pushes out the burnt gases through the exhaust valve. This clears the cylinder for the next cycle. The engine repeats these steps quickly to keep running smoothly and powerfully.
Efficiency Factors
Diesel engines are known for their strong performance and fuel savings. Their efficiency depends on several key factors. These factors help diesel engines use fuel better and produce more power. Understanding these can show why diesel engines often outperform gasoline engines in many ways.
High Compression Ratio
Diesel engines use a high compression ratio. This means they squeeze air inside the cylinder very tightly. The air gets very hot from this pressure. Fuel injected into the hot air ignites by itself. This process avoids the need for spark plugs. High compression improves engine power and cuts fuel waste.
Fuel Economy Benefits
Diesel fuel contains more energy than gasoline. This gives diesel engines better fuel economy. They need less fuel to travel the same distance. Diesel engines also run at lower engine speeds. This lowers fuel consumption and reduces wear on engine parts.
Thermal Efficiency
Diesel engines convert more heat from fuel into mechanical energy. This is called thermal efficiency. Better thermal efficiency means less fuel is lost as heat. The engine stays cooler and runs longer without overheating. This helps save fuel and extend engine life.
Advantages Over Gasoline Engines
Diesel engines have clear benefits compared to gasoline engines. These advantages make them popular in many vehicles and machines. Understanding these benefits helps explain why diesel engines are widely used.
Torque And Power Output
Diesel engines produce more torque at low speeds. This means they can move heavy loads easily. Trucks and buses use diesel for this reason. High torque helps with towing and carrying weight. Gasoline engines usually have lower torque at low RPMs.
Durability And Longevity
Diesel engines are built stronger to handle high compression. This makes them last longer than gasoline engines. Many diesel engines run over 300,000 miles without major repairs. Their tough parts resist wear and tear better. This durability reduces the need for frequent maintenance.
Fuel Type And Availability
Diesel fuel contains more energy per gallon than gasoline. This leads to better fuel efficiency in diesel engines. Diesel is widely available, especially for commercial vehicles. Many places offer diesel at fuel stations worldwide. Diesel engines also work well with biodiesel, a renewable fuel option.
Common Applications
Diesel engines power many types of machines and vehicles worldwide. Their strong performance and fuel efficiency make them popular for tough jobs. These engines work well in different settings.
Below are some common uses of diesel engines. Each area benefits from their unique strengths.
Automotive Uses
Diesel engines are common in trucks and buses. They provide the power needed for heavy loads and long trips. Many cars in Europe use diesel for better mileage. Diesel engines last longer and need less fuel than gasoline engines.
Industrial And Heavy Machinery
Construction machines like bulldozers and excavators often use diesel engines. They give strong torque and steady power for hard work. Factories also use diesel generators to keep running during power cuts. These engines handle tough conditions well.
Marine And Aviation
Large ships rely on diesel engines for long journeys at sea. Diesel fuel is safer and easier to store on boats. Some small airplanes use diesel engines for better fuel economy. Their reliability is important in both marine and air travel.
Recent Innovations
Diesel engines have changed a lot in recent years. New technologies make them cleaner and more efficient. These improvements help reduce pollution and save fuel. Many changes focus on how fuel burns and how engines handle emissions. The goal is to keep diesel engines useful and better for the environment.
Emission Reduction Technologies
New filters and catalysts lower harmful gases from diesel engines. Devices like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) trap soot before it leaves the exhaust. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) uses a special fluid to cut nitrogen oxide emissions. These tools help engines meet strict pollution rules. Cleaner air from diesel engines means less harm to health and nature.
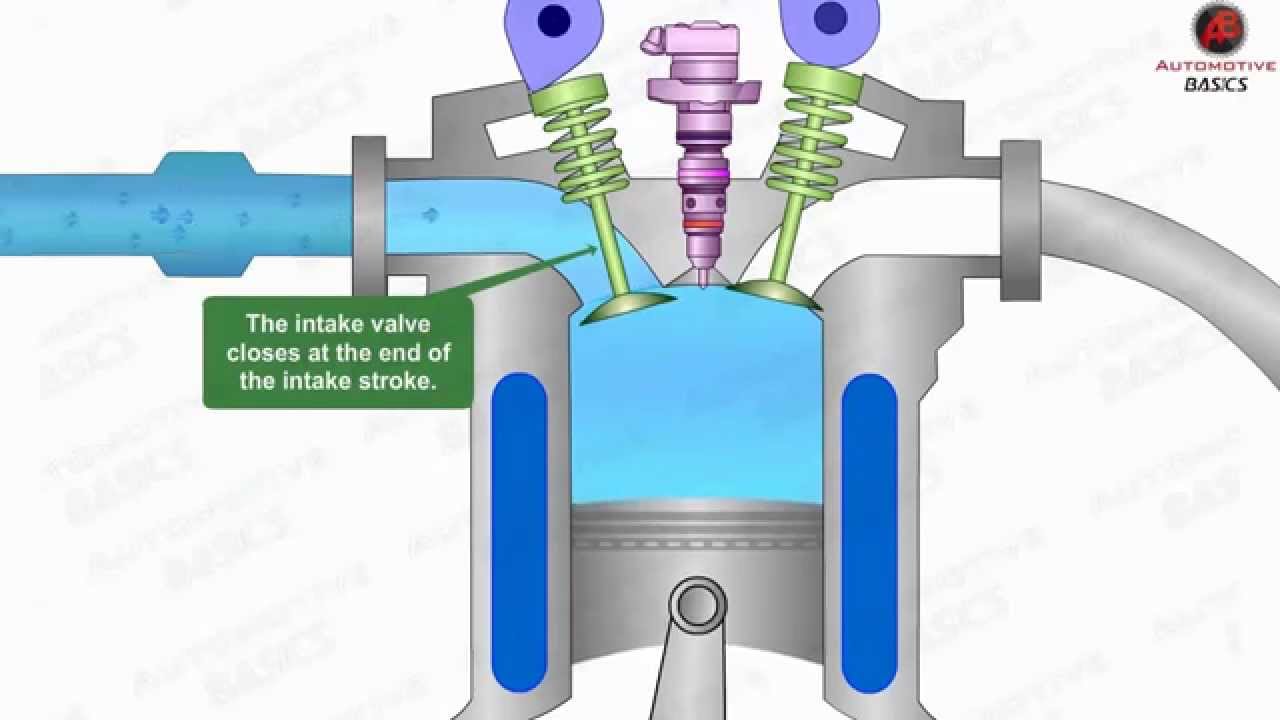
Advanced Fuel Injection Systems
Modern diesel engines use precise fuel injection to improve performance. High-pressure injectors spray fuel in tiny droplets for better mixing with air. This leads to more complete burning of fuel. Better fuel use means more power and less waste. New systems adjust injection timing to match driving conditions. This keeps engines running smoothly and efficiently.
Hybrid Diesel Powertrains
Combining diesel engines with electric motors creates hybrid powertrains. These systems use electric power to help during low speeds or start-up. The diesel engine runs less often, saving fuel and cutting emissions. Regenerative braking stores energy when slowing down. Hybrid diesel vehicles offer a balance of power and efficiency. This tech supports cleaner transport while keeping diesel’s strength.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Diesel Engines Ignite Fuel Without Spark Plugs?
Diesel engines ignite fuel through compression. Air is highly compressed, raising temperature. Injected diesel fuel then auto-ignites due to this heat, eliminating the need for spark plugs.
What Makes Diesel Engines More Fuel-efficient?
Diesel engines use higher compression ratios and leaner fuel mixtures. This improves combustion efficiency, leading to better fuel economy than gasoline engines.
Why Are Diesel Engines Preferred For Heavy Vehicles?
Diesel engines deliver higher torque at low RPMs. This provides better pulling power and durability, ideal for trucks, buses, and heavy machinery.
How Does The Fuel Injection System Work In Diesel Engines?
The fuel injection system sprays precise amounts of diesel into compressed air. This ensures efficient combustion and optimal engine performance.
Conclusion
Diesel engines use air compression to ignite fuel without sparks. They are strong and efficient for many vehicles and machines. These engines burn fuel slowly, saving energy and reducing waste. Understanding their process helps you appreciate their design. Diesel engines stay popular because they last long and use less fuel.
Knowing how they work makes it easier to maintain them. Simple parts work together to power trucks, boats, and generators. Diesel engines play a big role in transport and industry today.