Have you ever wondered what happens inside your car engine when you turn the key? Understanding how a car engine works can seem complicated, but it’s easier than you think.
When you know the step-by-step process, you’ll see how every part plays a role in making your car move. This knowledge can help you take better care of your vehicle and even impress your friends with some cool facts. Keep reading, and you’ll discover exactly how your car engine powers your drive from start to finish.
Basic Engine Components
Understanding the basic parts of a car engine helps you see how it works. Each part has a clear job. Together, they make the engine run smoothly. This section explains the main components inside the engine.
Engine Block
The engine block is the engine’s main frame. It holds all the other parts in place. Made from strong metal, it needs to handle heat and pressure. Inside, it has spaces for cylinders and passages for coolant.
Pistons And Cylinders
Pistons move up and down inside the cylinders. Each cylinder is a hollow tube in the engine block. The piston’s movement creates power by compressing fuel and air. This power pushes the piston down to turn the crankshaft.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft changes the pistons’ up-and-down motion into spinning motion. It is connected to the pistons by rods. This spinning motion moves the car’s wheels through the transmission system.
Camshaft
The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. It spins at half the speed of the crankshaft. Its lobes push the valves at the right time for air and fuel to enter and exit.
Valves And Timing
Valves let air in and exhaust gases out of the engine. Their timing is very important. Valves open and close at exact moments to keep the engine working well. The camshaft and timing belt or chain manage this timing.
Four-stroke Cycle
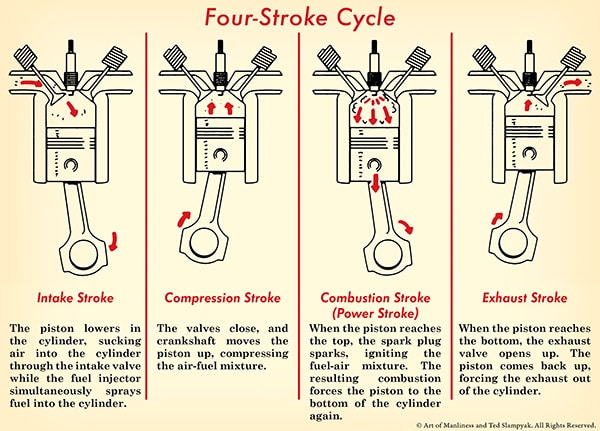
The four-stroke cycle is the heart of most car engines. It turns fuel into power through four main steps. Each step moves the engine parts to keep the car running. Understanding these strokes helps you see how your engine works inside.
Intake Stroke
The intake stroke starts the process. The piston moves down, making space inside the cylinder. The intake valve opens, letting air and fuel mix enter. This mixture is key to creating energy later. The piston’s movement fills the cylinder with the fuel-air mix.
Compression Stroke
Next is the compression stroke. The piston moves up, squeezing the fuel and air mix. This makes the mix dense and ready to ignite. Both valves stay closed to keep the mix inside. Compressed fuel burns faster and creates more power.
Power Stroke
The power stroke is where energy is made. A spark from the spark plug lights the compressed mix. It explodes, pushing the piston down hard. This push turns the engine’s crankshaft. The engine uses this power to move the car forward.
Exhaust Stroke
The last step is the exhaust stroke. The piston moves up again. The exhaust valve opens, letting out burnt gases. These gases leave the cylinder through the exhaust system. This clears the cylinder for the next cycle to start fresh.
Fuel Injection And Air Intake
The fuel injection and air intake system plays a key role in how a car engine works. It controls the flow of fuel and air into the engine’s cylinders. Proper mixing of fuel and air helps the engine run smoothly and efficiently.
This system replaces old carburetors in most modern cars. It uses sensors and precise controls to deliver the right amount of fuel. The engine then burns this mixture to create power.
Fuel Delivery Methods
Fuel injection delivers fuel directly into the engine’s intake or cylinders. There are different types, like port injection and direct injection. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold. Direct injection sprays fuel straight into the combustion chamber. Both methods improve fuel use and engine response.
Air-fuel Mixture
The air-fuel mixture is a blend of air and fuel that the engine burns. The ratio between air and fuel is very important. Too much fuel causes pollution and wastes fuel. Too little fuel causes poor engine power. Sensors monitor this mix to keep it balanced for clean and efficient running.
Throttle Control
The throttle controls the amount of air entering the engine. When you press the gas pedal, the throttle opens wider. This lets more air in, so the engine burns more fuel and makes more power. Modern cars use electronic throttle control for precise air flow. This helps with better fuel efficiency and smoother driving.
Ignition Process
The ignition process is a key step in how a car engine works. It starts the engine by creating a spark that lights the fuel-air mix. This spark causes a small explosion, pushing the piston down. This movement powers the car.
The ignition process must happen at the right moment. If it is too early or too late, the engine runs poorly. The system includes parts working together to create and time the spark.
Spark Plug Function
The spark plug creates the spark inside the engine’s cylinder. It has two metal electrodes with a small gap between them. The spark jumps across this gap, igniting the fuel-air mix. Spark plugs must be strong and heat resistant. They wear out over time and need replacement to keep the engine running smooth.
Timing Of Ignition
Ignition timing controls when the spark happens during the piston’s movement. The spark must occur just before the piston reaches the top of its stroke. This timing lets the fuel burn fully and push the piston down with power. Modern engines use sensors and computers to adjust timing. Proper timing improves fuel efficiency and engine performance.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system plays a vital role in a car engine. It removes harmful gases produced during combustion. This system keeps the engine running smoothly and reduces pollution.
Each part of the exhaust system has a special job. Together, they guide exhaust gases safely out of the car. Let’s explore the main components step by step.
Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold collects gases from the engine cylinders. It connects directly to the engine block. This part directs hot gases into one pipe. The manifold is usually made of cast iron or steel. It must handle very high temperatures without cracking.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter cleans the exhaust gases. It changes harmful chemicals into less harmful ones. Inside, a catalyst helps speed up this process. It reduces carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. This part is important for meeting pollution laws.
Muffler
The muffler lowers the noise from exhaust gases. It uses chambers and tubes to reduce sound waves. Without a muffler, the engine would be very loud. It also helps the gases flow smoothly out of the tailpipe.

Cooling System
The cooling system keeps the engine from getting too hot. It stops damage caused by high temperatures. The system uses water and coolant fluid to absorb heat. This heat moves away from the engine to keep it safe.
Radiator Role
The radiator cools the hot coolant from the engine. It has many small tubes and fins. Air passes through these fins and lowers the coolant temperature. The cooled liquid goes back to the engine to absorb more heat.
Coolant Flow
Coolant moves through the engine and radiator in a loop. It picks up heat from the engine’s metal parts. The pump pushes the coolant through the system quickly. This constant flow keeps the engine temperature steady.
Thermostat Function
The thermostat controls when coolant moves to the radiator. It stays closed when the engine is cold. This helps the engine warm up fast. When the engine gets hot, the thermostat opens. It lets coolant flow to the radiator for cooling.
Lubrication System
The lubrication system is a key part of a car engine. It keeps the engine parts moving smoothly and stops them from wearing out. Without oil, the engine would get very hot and break down quickly.
This system moves oil to all the parts that need it. The oil reduces friction and cools the engine. It also helps clean away dirt and tiny metal pieces.
Oil Pump
The oil pump pushes oil through the engine. It works like a heart, sending oil to all the parts. The pump makes sure oil flows fast enough to protect the engine.
It starts working as soon as the engine runs. If the oil pump stops, the engine parts will rub and get damaged.
Oil Filter
The oil filter cleans the oil before it reaches the engine parts. It traps dirt, dust, and metal bits. This keeps the oil clean and the engine safe.
A dirty filter can block oil flow. That can cause engine problems. Changing the oil filter regularly is very important.
Lubrication Points
Lubrication points are the engine parts that need oil. These include the crankshaft, camshaft, pistons, and valves. Oil forms a thin layer between these parts.
This layer stops metal from rubbing directly. It helps the engine run quietly and last longer. Every engine part that moves needs oil at these points.
Engine Performance Factors
Engine performance depends on several key factors. These factors affect how power is created and used. Understanding them helps explain how engines work efficiently. Each plays a vital role in the engine’s overall function and output.
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio is the volume difference in the cylinder. It measures the air and fuel mix before ignition. A higher ratio means better power and efficiency. But too high can cause engine knocking. Correct balance is crucial for smooth performance.
Air-fuel Ratio
This ratio shows the amount of air compared to fuel. Proper mix ensures complete combustion. Too much fuel causes pollution and wastes gas. Too little fuel leads to weak engine power. The perfect balance keeps the engine running clean and strong.
Engine Timing
Engine timing controls when the spark ignites the fuel. Proper timing means the spark fires at the right moment. Early or late sparks reduce power and cause damage. Correct timing improves fuel use and lowers emissions. It keeps the engine running smoothly and efficiently.
Common Engine Types
Car engines come in different shapes and sizes. Each type has a unique design that affects how the engine runs and how the car performs. Understanding common engine types helps you know more about your vehicle and its power.
Most engines are built with cylinders arranged in specific ways. This arrangement affects the engine’s balance, smoothness, and size. The three common engine types are inline, V, and boxer engines.
Inline Engines
Inline engines have all cylinders arranged in a straight line. This layout is simple and cost-effective. It fits well in small engine bays and is easy to maintain. Many compact cars use inline engines because they are light and efficient.
V Engines
V engines have cylinders arranged in two banks forming a “V” shape. This design makes the engine shorter but wider. V engines can have more cylinders, which means more power. They are common in sports cars and trucks for strong performance.
Boxer Engines
Boxer engines have cylinders lying flat in two banks opposite each other. The pistons move horizontally, which lowers the engine’s center of gravity. This helps improve car stability and handling. Subaru and Porsche often use boxer engines for smooth rides.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Does A Car Engine Start Working?
A car engine starts by igniting fuel inside cylinders. The spark plug lights the air-fuel mix, creating combustion. This process powers pistons, turning the crankshaft and starting engine operation.
What Are The Main Parts Of A Car Engine?
Key engine parts include pistons, cylinders, spark plugs, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, and the fuel injector. Each part works together to convert fuel into mechanical power.
How Does Combustion Power A Car Engine?
Combustion occurs when the spark plug ignites fuel and air. This explosion pushes pistons down, creating mechanical energy. The energy turns the crankshaft, powering the car’s movement.
Why Is The Four-stroke Cycle Important In Engines?
The four-stroke cycle—intake, compression, power, exhaust—ensures efficient fuel burning. Each stroke manages air and fuel flow, combustion, and exhaust removal. This cycle maximizes engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding how a car engine works helps you appreciate your vehicle more. Each step plays a vital role in making the engine run smoothly. From air intake to exhaust, parts work together in a cycle. Knowing these basics can help with simple maintenance tasks.
It also makes car troubles less confusing. A clear grasp of engine steps builds confidence for any driver. Keep exploring to learn more about your car’s parts and functions. Simple knowledge makes driving safer and more enjoyable.



