Have you ever wondered what powers your car or motorcycle? The answer lies in something called an internal combustion engine.
This powerful device is at the heart of many machines you use every day, turning fuel into motion. But what exactly is an internal combustion engine, and how does it work? Understanding this can give you a new appreciation for the technology that moves you.
Keep reading, and you’ll discover the simple science behind this engine that drives so much of your world.

Internal Combustion Engine Basics
The internal combustion engine is a key part of many vehicles today. It changes fuel into energy to move cars, motorcycles, and trucks. Understanding how it works helps us see why it is so important in daily life.
This engine burns fuel inside a small space called a cylinder. The burning creates pressure, which moves parts inside the engine. This movement then powers the wheels or other machinery.
Core Components
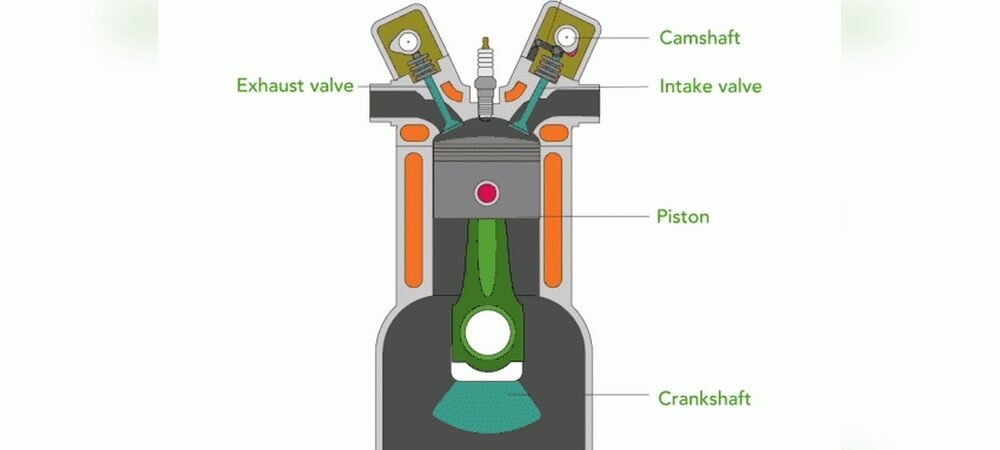
Several main parts make up an internal combustion engine. The cylinder is where fuel burns. The piston moves up and down inside the cylinder. The spark plug lights the fuel. The crankshaft changes the piston’s motion into rotary motion. These parts work together to create power.
Types Of Engines
There are different types of internal combustion engines. The two main types are gasoline engines and diesel engines. Gasoline engines use a spark to ignite fuel. Diesel engines compress air to heat it, then inject fuel. Each type has its own uses and benefits.
How It Generates Power
Power is made through a process called combustion. Fuel mixes with air inside the cylinder. The spark plug ignites this mixture, causing a small explosion. This pushes the piston down. The piston moves the crankshaft, which turns the wheels. This cycle repeats many times per second to keep the engine running.

Fuel And Combustion Process
The fuel and combustion process is the heart of an internal combustion engine. It turns fuel into energy that powers vehicles and machines. Understanding this process helps us see how engines work efficiently. It also explains why different fuels affect performance and emissions.
Fuel Types Used
Internal combustion engines use various fuels. Gasoline is the most common for cars and motorcycles. Diesel fuel is popular in trucks and heavy equipment. Some engines run on alternative fuels like ethanol, propane, or natural gas. Each fuel type has unique properties that influence engine design and operation.
Combustion Cycle Explained
The combustion cycle has four main steps: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. During intake, the engine draws in air and fuel. Compression squeezes the air-fuel mix to prepare for ignition. The power stroke ignites the mixture, creating an explosion. Exhaust pushes out the burned gases to make room for fresh air and fuel.
Air-fuel Mixture Role
The air-fuel mixture is critical for efficient combustion. The right balance ensures complete burning of fuel. Too much fuel causes waste and pollution. Too much air lowers power and can cause misfires. Modern engines use sensors to keep this mix just right for better fuel economy and fewer emissions.
Engine Performance Factors
Engine performance factors determine how well an internal combustion engine works. These factors affect power, fuel use, and the pollution the engine creates. Understanding these elements helps in choosing or improving an engine.
Power Output
Power output shows how much work the engine can do. It depends on the engine size and design. More power means faster speeds and better towing ability. Power is measured in horsepower or kilowatts.
Efficiency And Emissions
Efficiency tells us how well the engine uses fuel. A more efficient engine saves fuel and costs less to run. Emissions are gases released when the engine burns fuel. Lower emissions mean less harm to the air and environment.
Common Performance Metrics
Performance metrics include torque, horsepower, and fuel consumption. Torque measures the engine’s twisting force. It affects acceleration and load carrying. Fuel consumption shows how much fuel the engine uses per distance. These metrics help compare different engines.

Cooling And Lubrication Systems
The internal combustion engine produces a lot of heat and friction while running. Cooling and lubrication systems keep the engine working well. They stop the engine from overheating and reduce wear on its parts. These systems help the engine last longer and run smoothly.
Cooling Methods
Cooling systems remove extra heat from the engine. Air cooling uses air flow to cool engine parts. It is simple and common in small engines. Water cooling uses liquid coolant to carry heat away. A radiator helps cool the liquid before it returns. This method is common in cars and trucks. Both methods keep the engine temperature safe.
Lubrication Importance
Lubrication reduces friction between moving engine parts. Oil spreads over parts to stop metal from rubbing. This lowers heat and prevents damage. Oil also helps clean engine parts by carrying dirt away. Without lubrication, engine parts wear out quickly. Proper lubrication keeps the engine running quietly and efficiently.
Maintaining Engine Health
Regularly checking coolant and oil levels is key. Old oil or low coolant can cause engine damage. Changing oil and coolant on time keeps the system healthy. Clean filters also help lubrication and cooling work well. These simple steps protect the engine and save repair costs. Healthy engines perform better and last longer.
Advancements In Engine Technology
Advancements in engine technology have made internal combustion engines more efficient and cleaner. These improvements help engines use less fuel and produce fewer emissions. Innovations in design and parts have also increased power and performance. The following sections explore key developments that shape modern engines.
Fuel Injection Systems
Fuel injection systems deliver fuel directly into the engine’s combustion chamber. This method replaces older carburetor systems. It controls fuel flow with high precision. This leads to better fuel efficiency and lower emissions. Electronic fuel injection adjusts fuel based on engine conditions. It improves engine response and reduces waste.
Turbocharging And Supercharging
Turbocharging uses exhaust gases to increase air intake pressure. This adds more oxygen to the engine for better combustion. Supercharging uses a belt-driven compressor to force air into the engine. Both methods boost engine power without increasing engine size. They help smaller engines produce more power and save fuel.
Hybrid And Alternative Engines
Hybrid engines combine internal combustion with electric power. This reduces fuel use and pollution. Alternative engines use fuels like hydrogen or biofuels. These fuels emit fewer harmful gases. Advances in battery technology support hybrid and electric engines. These changes offer cleaner and more efficient options for vehicles.
Applications Of Internal Combustion Engines
Internal combustion engines power many machines and vehicles. They convert fuel into energy through controlled explosions inside the engine. This energy then moves parts and creates motion. These engines have many uses across different fields.
They are common in cars, boats, and machines that produce electricity. The engines vary in size and power depending on the need. Their versatility makes them important in daily life and work.
Automotive Use
Most cars use internal combustion engines. These engines burn gasoline or diesel fuel. This creates power to move the vehicle forward. The engines fit well in cars because they are compact and efficient. They help cars reach high speeds and travel long distances. Many trucks and motorcycles also use these engines.
Industrial And Marine Engines
Large internal combustion engines run heavy machines in factories. They power construction equipment like bulldozers and cranes. In the marine world, these engines drive ships and boats. They provide strong and steady power needed on water. Diesel engines are common for big ships because they are reliable and fuel-efficient.
Power Generation
Internal combustion engines generate electricity in many places. They work in power plants and backup generators. These engines start quickly and provide power during outages. Small engines can power remote homes or tools. Larger engines support industrial electricity needs. Their ability to produce power on demand is valuable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Internal Combustion Engine?
An internal combustion engine burns fuel inside its cylinders to create power. This process drives pistons, generating mechanical energy to move vehicles or machinery efficiently.
How Does An Internal Combustion Engine Work?
Fuel mixes with air and ignites inside the engine’s cylinder. This explosion pushes a piston, converting chemical energy into mechanical motion.
What Are Common Fuels For Internal Combustion Engines?
Gasoline, diesel, natural gas, and ethanol are common fuels. Each fuel type affects engine performance, efficiency, and emissions differently.
What Are The Main Parts Of An Internal Combustion Engine?
Key components include cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, valves, and spark plugs. These parts work together to convert fuel energy into motion.
Conclusion
Internal combustion engines power many machines we use daily. They burn fuel inside to create energy. This energy moves cars, motorcycles, and even some boats. Understanding how they work helps us appreciate modern technology. Though they have limits, they remain important in transport.
Cleaner alternatives are growing but engines still play a big role. Knowing this engine’s basics connects us to how things move. Simple yet powerful – that’s the internal combustion engine.