Have you ever wondered who invented the internal combustion engine—the very heart of most cars and machines you see every day? Understanding this invention can change the way you see modern technology.
Knowing the story behind it connects you to a moment that transformed how we move, work, and live. Keep reading, and you’ll discover surprising facts and the clever minds that made it all possible. This isn’t just history; it’s the key to understanding the world around you.

Early Concepts Of Combustion Engines
The idea of using combustion to create power is very old. People have been curious about how fire and air can move machines. Early inventors and thinkers tried many ways to use burning fuel to make motion. Their work laid the base for the engines we use today. This section explores the first ideas and experiments that led to the internal combustion engine.
Ancient Innovations
Long ago, around the first century AD, Hero of Alexandria made a simple steam engine. It used steam from boiling water to spin a small wheel. This device showed how heat could turn into motion. Although it did not burn fuel inside a cylinder, it inspired later ideas about engines. Other ancient cultures also used fire and air to power tools and toys.
17th Century Experiments
In the 1600s, inventors began testing ways to burn fuel inside a closed space. They tried using gunpowder and air to push pistons. Some early models used small explosions to create movement. Scientists like Christiaan Huygens built early engines powered by gunpowder. These machines were rough but showed the power of controlled explosions. Their work pointed toward engines using fuel and air inside cylinders.

Pioneers Of The Internal Combustion Engine
The internal combustion engine changed the world. It powers cars, trucks, and many machines. This invention did not come from one person. Several pioneers made key discoveries that built the engine we know today.
Each pioneer brought new ideas. They worked on different parts of the engine. Their work laid the foundation for modern engines. Understanding their contributions helps us appreciate this important invention.
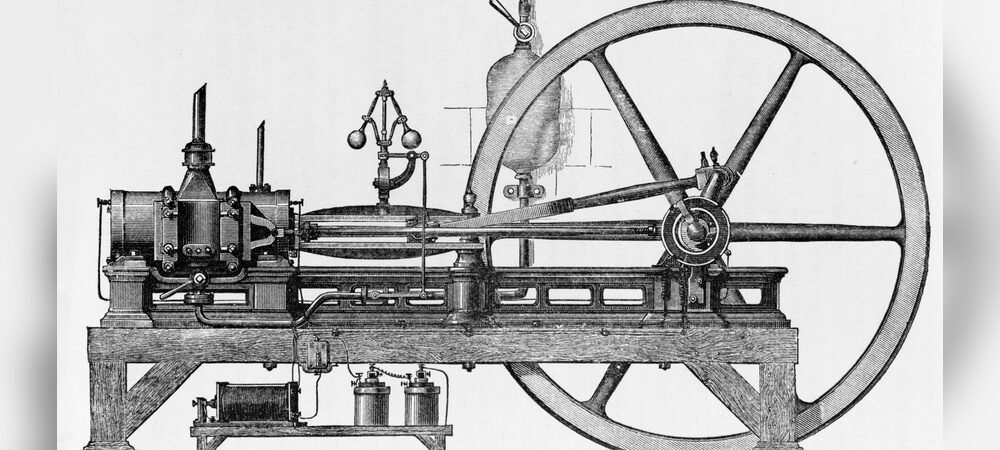
Nikolaus Otto’s Breakthrough
Nikolaus Otto created the first practical four-stroke engine. This design improved efficiency and power. Otto’s engine used intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes. His work set the standard for most engines today. It made engines more reliable and useful.
Étienne Lenoir’s Contributions
Étienne Lenoir built one of the first internal combustion engines. His engine ran on coal gas in 1859. Lenoir’s design was simple but important. It showed that internal combustion was possible. His engine helped inspire future inventors.
Alphonse Beau De Rochas’ Principles
Alphonse Beau de Rochas developed key engine principles in 1862. He described the four-stroke cycle before Otto built his engine. Rochas focused on improving engine efficiency. His ideas guided engineers to better engine designs. His principles remain important in engine technology.
Advancements In Engine Design
The internal combustion engine improved a lot over time. Early designs were simple and less efficient. Inventors worked on making engines stronger and easier to use. These changes helped engines become common in cars and machines. Two big steps shaped engine design: the four-stroke cycle and better fuel and ignition systems.
These advancements made engines faster, cleaner, and more reliable. Understanding these changes shows how the engine grew into a key technology.
Four-stroke Cycle Development
The four-stroke cycle made engines work better. It uses four steps: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. This cycle helps the engine use fuel fully. Nikolaus Otto first built this engine in 1876. His design became the base for most modern engines. It gave more power and used less fuel. This made engines practical for cars and machines.
Fuel And Ignition Improvements
Early engines had trouble starting and running smoothly. Inventors improved fuel types and ignition methods. Spark plugs replaced less reliable ignition sources. Fuel became easier to burn and control. These changes helped engines start quickly and run cleaner. Better ignition systems allowed engines to work in cold weather. Fuel improvements also lowered engine noise and pollution.
Impact On Transportation And Industry
The invention of the internal combustion engine changed transportation and industry deeply. It brought new ways to move people and goods faster. It also made factories work better and grow larger. This engine helped shape the world in many ways.
Automobile Revolution
The internal combustion engine made cars practical and affordable. People could travel longer distances quickly and easily. Roads and highways expanded because more cars were on them. This change helped cities grow and connected towns far apart. It gave many people freedom to move on their own.
Industrial Applications
Factories began using internal combustion engines for power. Machines ran faster and worked more efficiently. This engine reduced the need for large, fixed power sources. Industries like farming, mining, and construction saw big improvements. The engine made tools and vehicles lighter and easier to use.
Controversies And Credit Disputes
The invention of the internal combustion engine is not credited to a single person. Several inventors contributed ideas and designs over many years. This created many debates about who truly deserves the credit. The story involves disputes, patent fights, and overlapping claims. These controversies have shaped how we view this important invention today.
Multiple Inventors Debate
Many inventors worked on early engine designs. Nikolaus Otto, Étienne Lenoir, and Nikolaus August Otto are often mentioned. Each created different versions of the engine. Some focused on improving efficiency. Others worked on fuel type or ignition methods. This led to confusion about who made the first true internal combustion engine. The debate continues among historians and engineers.
Patent Battles
Patent disputes complicated the credit issue further. Inventors filed patents to protect their designs. Some patents overlapped or copied ideas. Courts had to decide who owned the rights. These battles slowed development and caused tension. Patent wars highlighted the struggle for recognition. They also pushed inventors to create better, more original engines.
Legacy Of The Internal Combustion Engine
The internal combustion engine changed the world. It powers most cars, trucks, and machines today. Its invention sparked huge progress in transport and industry. This engine brought faster travel and easier goods movement. People could go farther and work more efficiently.
The legacy of the internal combustion engine is vast. It shaped modern life and technology. Its impact still drives innovation and challenges. Understanding this legacy helps us see future directions.
Modern Engine Technologies
Today’s engines are more advanced than ever. They use fuel injection for better power and less waste. Turbochargers help engines perform well with smaller sizes. Hybrid models combine electric and combustion power. This reduces fuel use and improves efficiency. Computer controls optimize engine timing and fuel flow. These tech improvements make engines cleaner and stronger.
Environmental Considerations
Engines affect air quality and climate. Burning fuel releases gases that harm the environment. Car makers work to lower emissions from engines. New rules push for cleaner exhaust standards. Electric vehicles rise as alternatives to reduce pollution. Research continues on biofuels and synthetic fuels. These aim to cut carbon footprints and protect the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who Invented The First Internal Combustion Engine?
Nikolaus Otto invented the first practical internal combustion engine in 1876. His four-stroke engine design revolutionized power generation. It efficiently converted fuel into mechanical energy, leading to modern engine development.
What Is The Significance Of Nikolaus Otto’s Invention?
Otto’s engine improved fuel efficiency and power output. It laid the foundation for gasoline engines used in cars today. This invention marked a major milestone in transportation technology.
How Did The Internal Combustion Engine Evolve After Otto?
After Otto, inventors like Diesel and Benz improved engine designs. Diesel introduced the compression ignition engine in 1893. Benz created the first car powered by an internal combustion engine. These advances boosted engine performance and usability.
Why Is The Internal Combustion Engine Important Today?
Internal combustion engines power most vehicles worldwide. They provide a reliable and compact power source. Despite electric alternatives, they remain essential for transportation and industry.
Conclusion
The internal combustion engine changed how we travel and work. Many inventors helped improve it over time. Nikolaus Otto is often called its key inventor. His engine design made cars and machines possible. This invention shaped modern life and industry.
Understanding its history helps appreciate today’s technology. The engine’s story shows how ideas grow and improve. The journey of invention never really ends.